Basic Example
Create a directory
Let's start by creating a working directory:
Write tungsten_model.py
You can write the tungsten_model.py file for an image classification model as follows:
import json
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List
import torch
from torchvision.models.mobilenetv2 import MobileNet_V2_Weights, MobileNetV2
from tungstenkit import BaseIO, Field, Image, define_model
LABELS = json.loads(Path("imagenet_labels.json").read_text())
class Input(BaseIO):
image: Image
class Output(BaseIO):
score: float
label: str = Field(choices=LABELS)
@define_model(
input=Input,
output=Output,
gpu=False,
python_packages=["torch", "torchvision"],
batch_size=16,
)
class Model:
def setup(self):
"""Load the model into memory"""
self.model = MobileNetV2()
weights = torch.load("mobilenetv2_weights.pth")
self.model.load_state_dict(weights)
self.model.eval()
def predict(self, inputs: List[Input]) -> List[Output]:
"""Run a batch prediction"""
print("Preprocessing")
transform = MobileNet_V2_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V2.transforms()
pil_images = [inp.image.to_pil_image() for inp in inputs]
tensors = [transform(img) for img in pil_images]
input_tensor = torch.stack(tensors, dim=0)
print("Inferencing")
softmax = self.model(input_tensor).softmax(1)
print("Postprocessing")
scores, class_indices = torch.max(softmax, 1)
pred_labels = [LABELS[idx.item()] for idx in class_indices]
return [
Output(score=score.item(), label=label) for score, label in zip(scores, pred_labels)
]
Download the required files
Before building, you should prepare the required files.
As you can see above, two files are needed: imagenet_labels.json and mobilenetv2_weights.pth.
Download these files via the script below:
curl -o imagenet_labels.json -X GET https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anishathalye/imagenet-simple-labels/master/imagenet-simple-labels.json && \
curl -o mobilenetv2_weights.pth https://download.pytorch.org/models/mobilenet_v2-7ebf99e0.pth
Build a Tungsten model
Now everything is ready. Let's start building a Tungsten model:
$ tungsten build -n tungsten-example
✅ Successfully built tungsten model: 'tungsten-example:e3a5de5616a743fe9021e2dcfe1cd19a' (also tagged as 'tungsten-example:latest')
$ tungsten models
Repository Tag Description Model Class Created Docker Image ID
---------------- -------------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------- ------------------- -----------------
tungsten-example latest Image classification model tungsten_model:Model 2023-04-26 05:23:58 830eb82f0fcd
tungsten-example e3a5de5616a743fe9021e2dcfe1cd19a Image classification model tungsten_model:Model 2023-04-26 05:23:58 830eb82f0fcd
Run it
Now, you can run the model in your local machine in multiple ways.
Option 1: Interactive web demo
Visit http://localhost:8080 to check: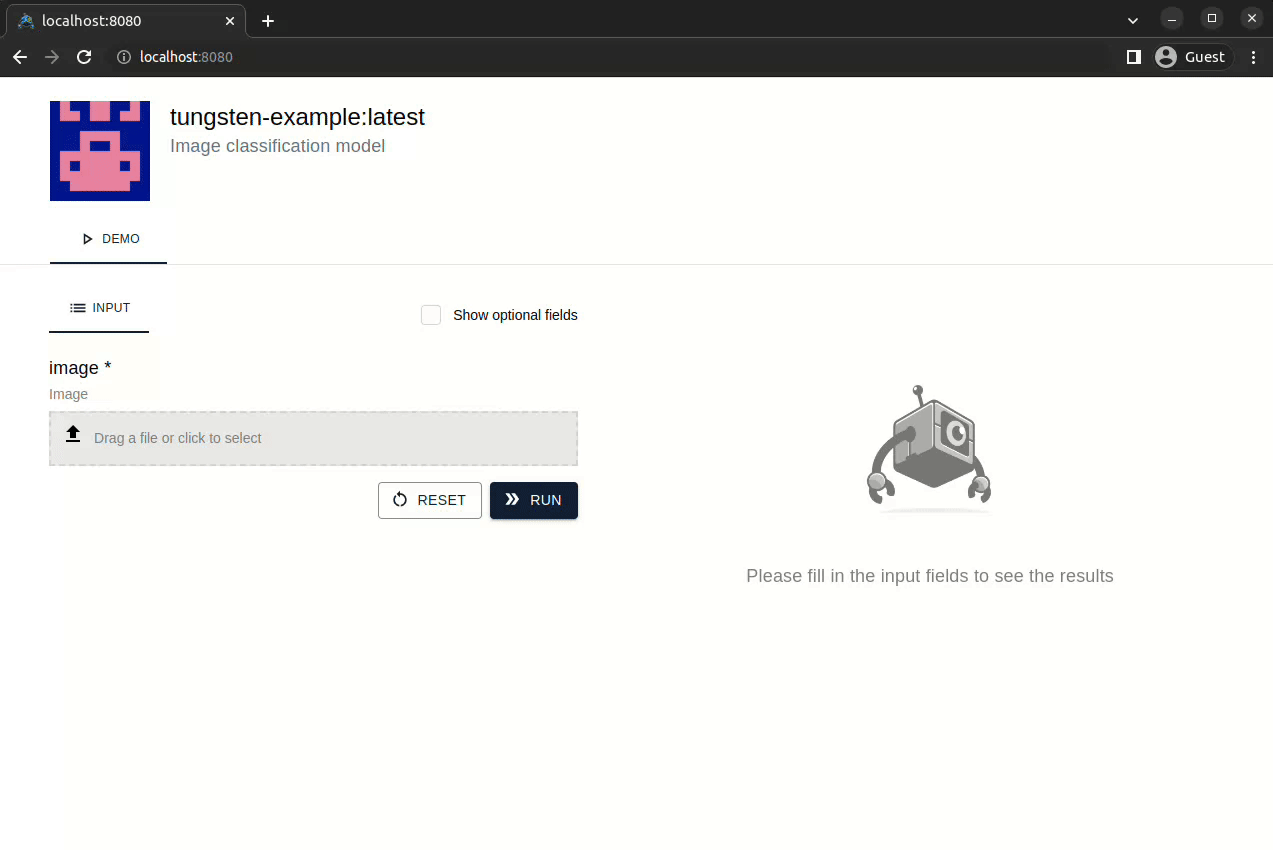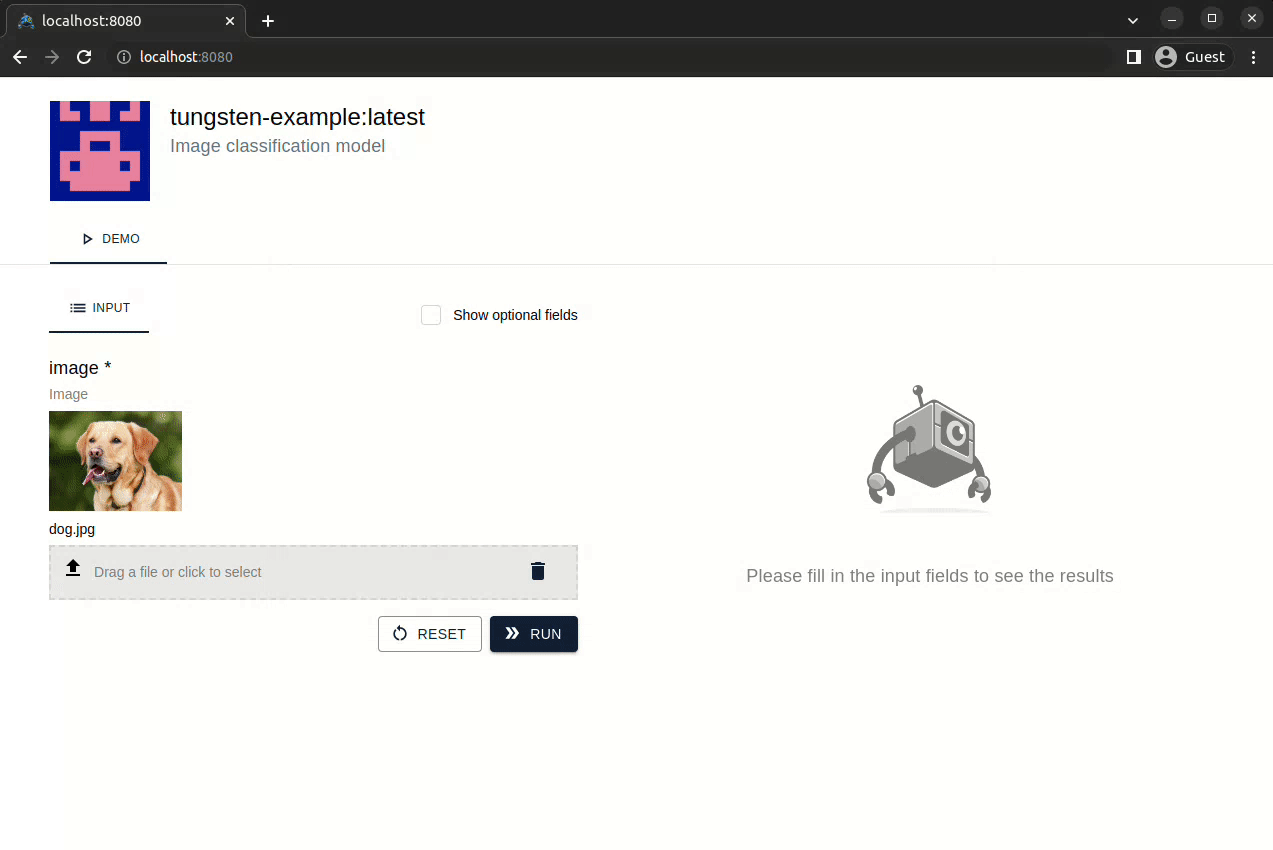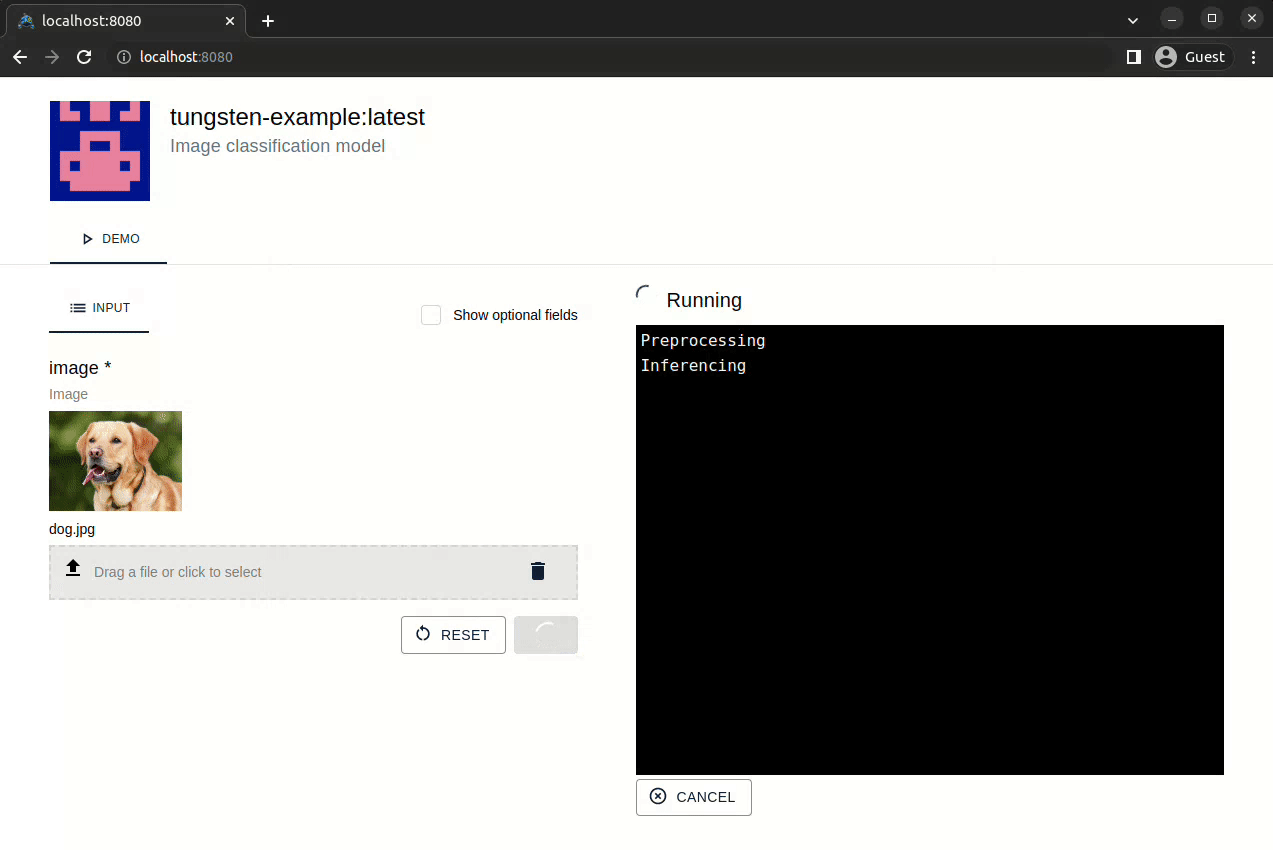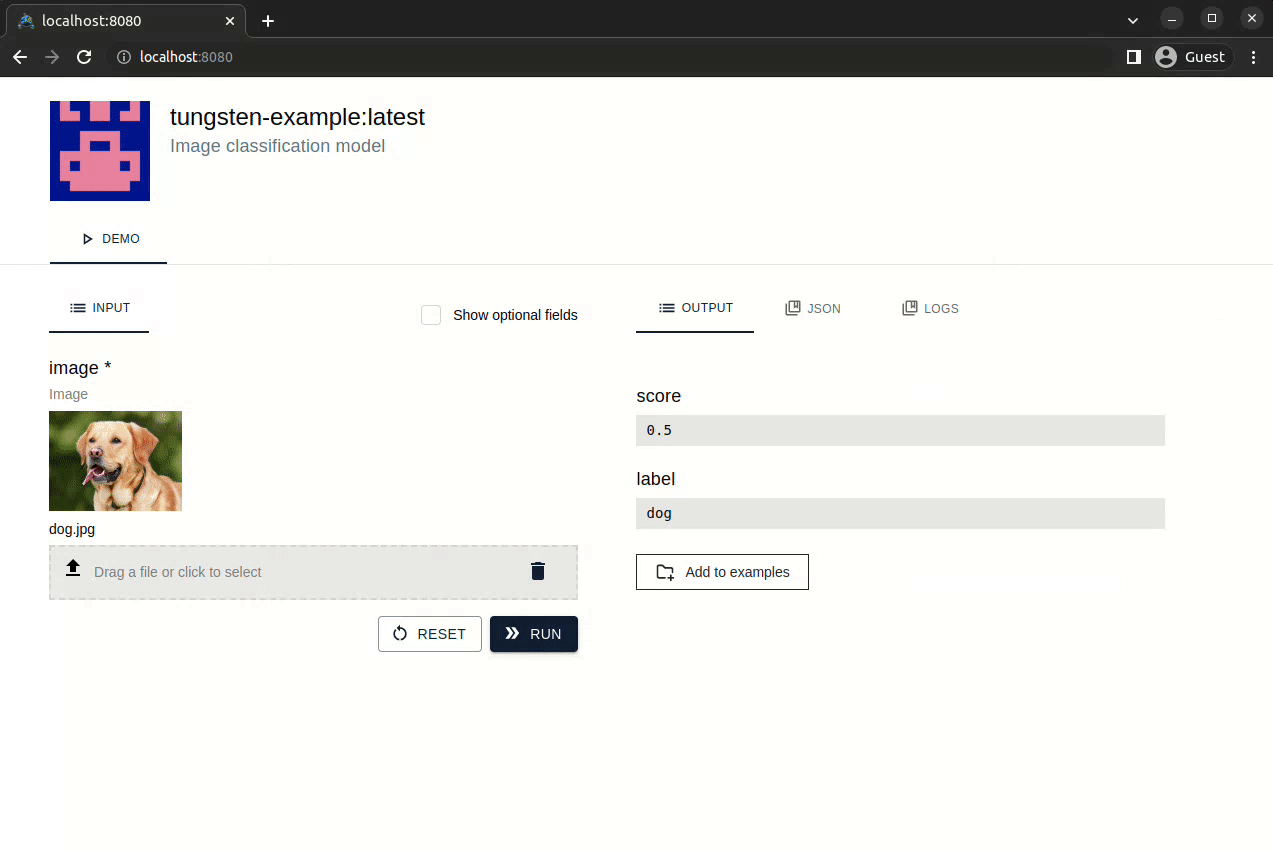
Option 2: REST API
Start the server:
$ tungsten serve tungsten-example -p 3000
INFO: Setting up the model
INFO: Getting inputs from the input queue
INFO: Starting the prediction service
INFO: Started server process [1]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:3000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Send a prediction request with a JSON payload:
$ curl -X 'POST' 'http://localhost:3000/predictions' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '[{"image": "https://picsum.photos/200.jpg"}]'
{
"prediction_id": "39c9eb6b"
}
Get the result:
$ curl -X 'GET' 'http://localhost:3000/predictions/39c9eb6b' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'
{
"outputs": [{"scale": 0.12483298, "label": "dog"}],
"status": "success"
}
Also, you can find a Swagger documentation at http://localhost:3000/docs.
Option 3: Make a prediction (using CLI)
$ tungsten predict tungsten-example -i image="https://picsum.photos/200.jpg"
{
"scale": 0.12483298, "label": "dog"
}